Peer Reviewed
Hepatic and Pulmonary Abscesses From Fusobacterium nucleatum Infection
AUTHORS:
Mariam Kirvalidze, DO
Family Practice Resident, Peconic Bay Medical Center, Riverhead, New YorkSandeep A. Gandhi, MD
Infectious Diseases Consultant at Peconic Bay Medical Center, Riverhead, New York, and Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine, Old Westbury, New YorkCITATION:
Kirvalidze M, Gandhi SA. Hepatic and pulmonary abscesses from Fusobacterium nucleatum infection. Consultant. 2020;60(2):57-58. doi:10.25270/con.2020.02.00006An 80-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, end-stage kidney disease on hemodialysis via a left arteriovenous fistula, and hypertension presented with a dry cough and had had a syncopal episode during a hemodialysis session.
Physical examination revealed a well-developed man with poor dentition. The remainder of the examination findings were unremarkable. Vital signs included a temperature of 37.2°C, a pulse of 76 beats/min, and a blood pressure of 104/50 mm Hg.
His white blood cell count was 20,200/μL with 89% neutrophils. The hemoglobin level was 9.2 g/dL, and the platelet count was 402 × 103/μL. Liver function test results were normal.
Chest radiography showed a new right lower lung mass. A chest computed tomography (CT) scan with contrast revealed a 3.7-cm cavitary lesion in the left upper lobe of the lung and an 8.3-cm necrotic-appearing cavitary lesion in the right lower lobe (Figure 1).

Figure 1. CT scan with contrast showing a right lower lung abscess.A subsequent CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis with contrast demonstrated a lung abscess and a 9.0-cm, multilocular, rim-enhancing liver abscess (Figure 2).

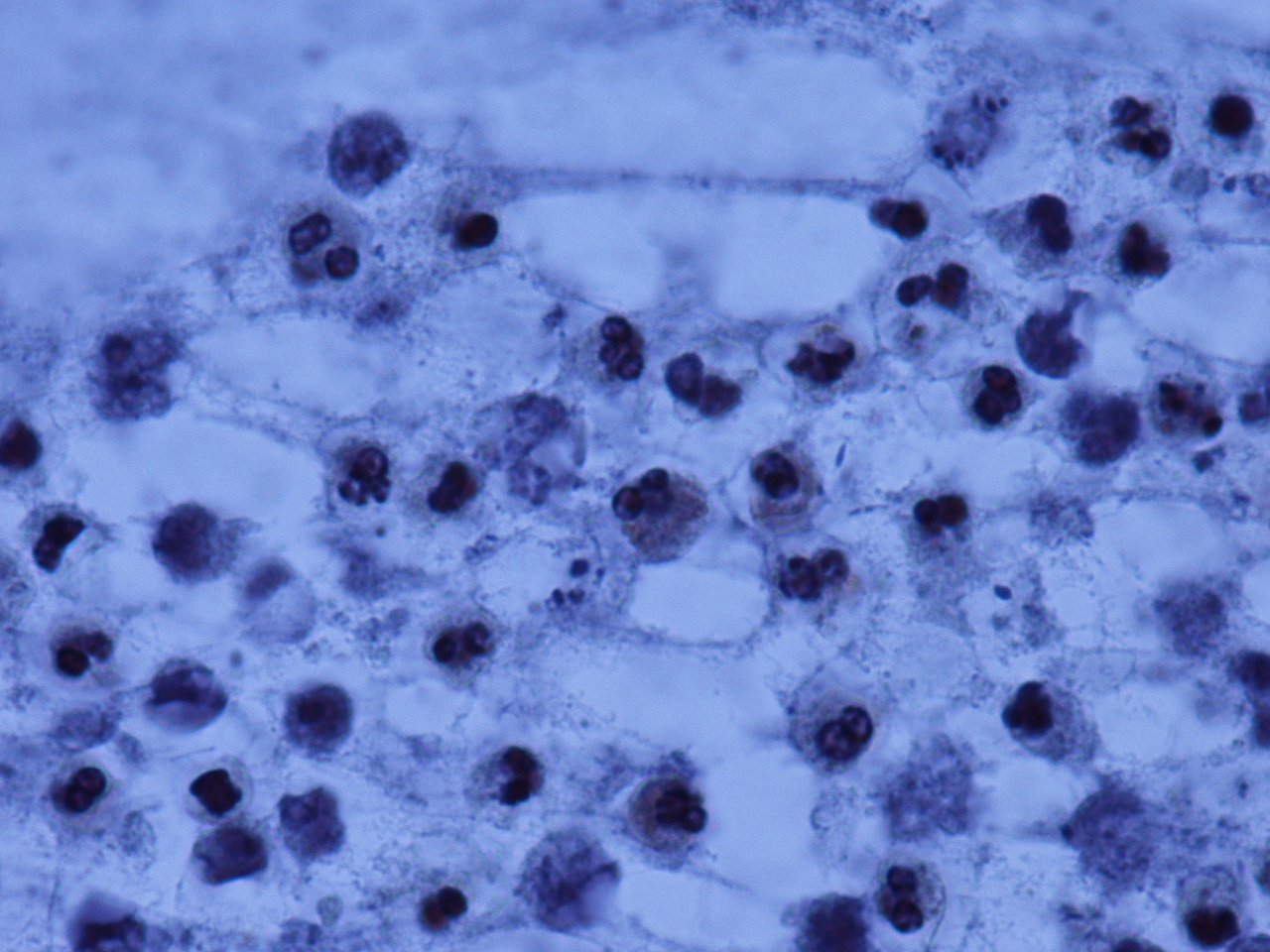
Figure 2. CT scan with contrast showing a multilocular, rim-enhancing liver abscess.Culture of the liver abscess grew Fusobacterium nucleatum, identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (Figure 3).

Figure 3. Hematoxylin-eosin stain of the liver abscess material, which grew Fusobacterium nucleatum (photo courtesy of Ranjana Mathur, MD).The hepatic abscess was drained by an interventional radiologist. The patient was treated with piperacillin-tazobactam and metronidazole until the abscesses had radiographically resolved.